Efficient Exploration in Constrained Environments with Goal-Oriented Reference Path
Published in IROS, 2020
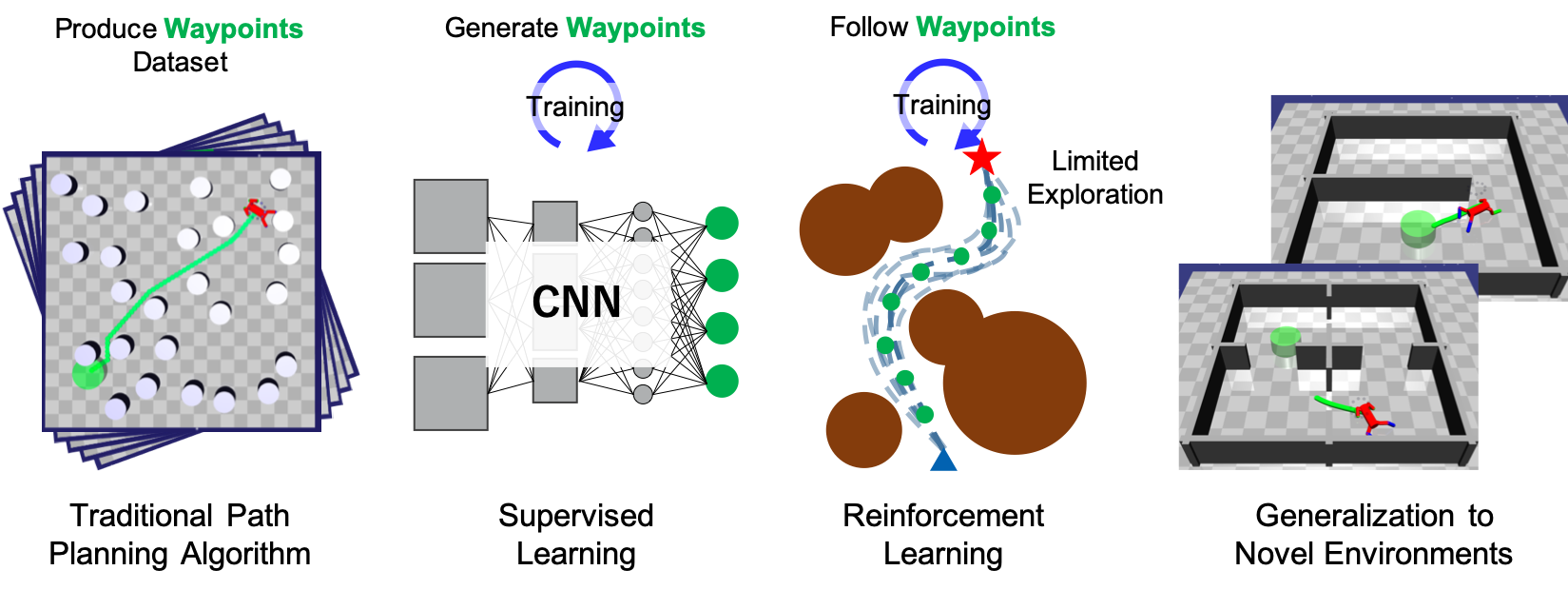
Designing RL agents that can learn complex, safe behavior in constrained environments for navigation has been getting a lot of attention recently. This has been mainly driven by the race to achieve artificial general intelligence where AI agents can achieve human-like performance. It is desirable that the RL agents can generalize to novel environments while achieving optimal performance. In this paper, we present a sample-efficient way of designing agents that can learn to generalize to different environments by combining classical planning algorithm, supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. The motivation of this combination comes from:
- generating optimal path on obstacle cluttered environment is easy using traditional path planning algorithm (A*, RRT, etc.)
- imitating the path (which we call waypoints) using SL is easy
- Waypoints that guides an RL agent to goal location makes easier to learn optimal policy by limiting exploration area
Below figure shows the architecture of the proposed method.
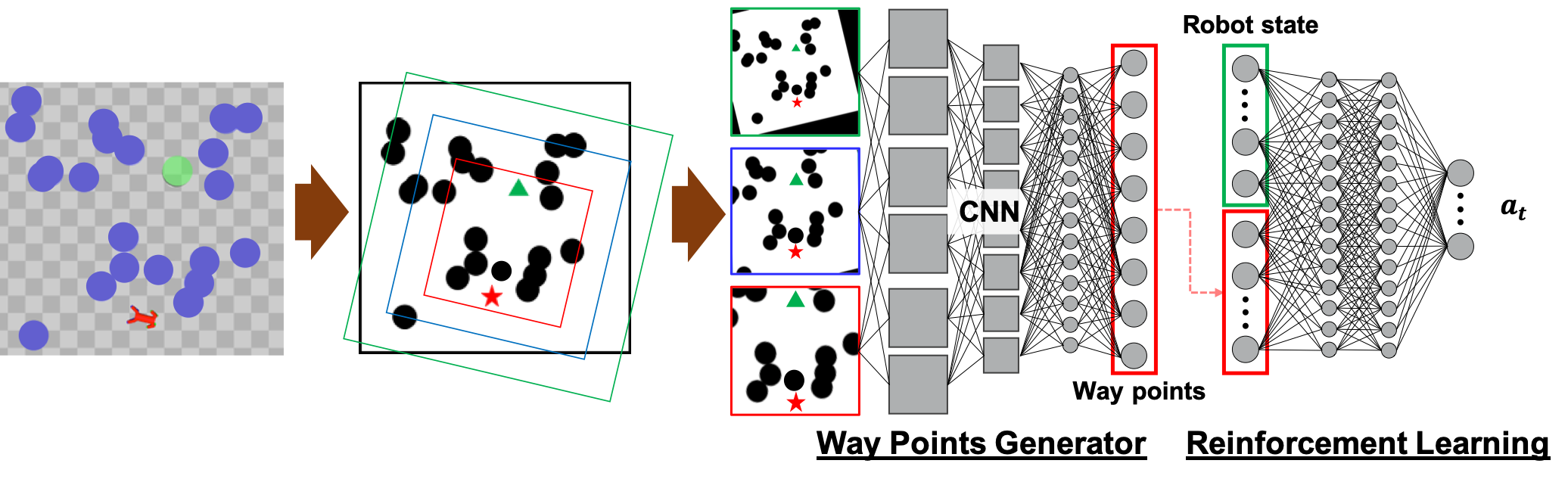
Then, how to exploit the waypoints? We use the similar technique with our previous research, that exploits the waypoints information to limit the search areas to explore for an RL agent as a form of reward function. The reward terms are: $w_1 d_{\rm path} + w_2 n_{\rm progress}$, essentially the first term penalizes to explore too far from waypoints, and second term encourages the agent to move toward a goal location along with the waypoints.
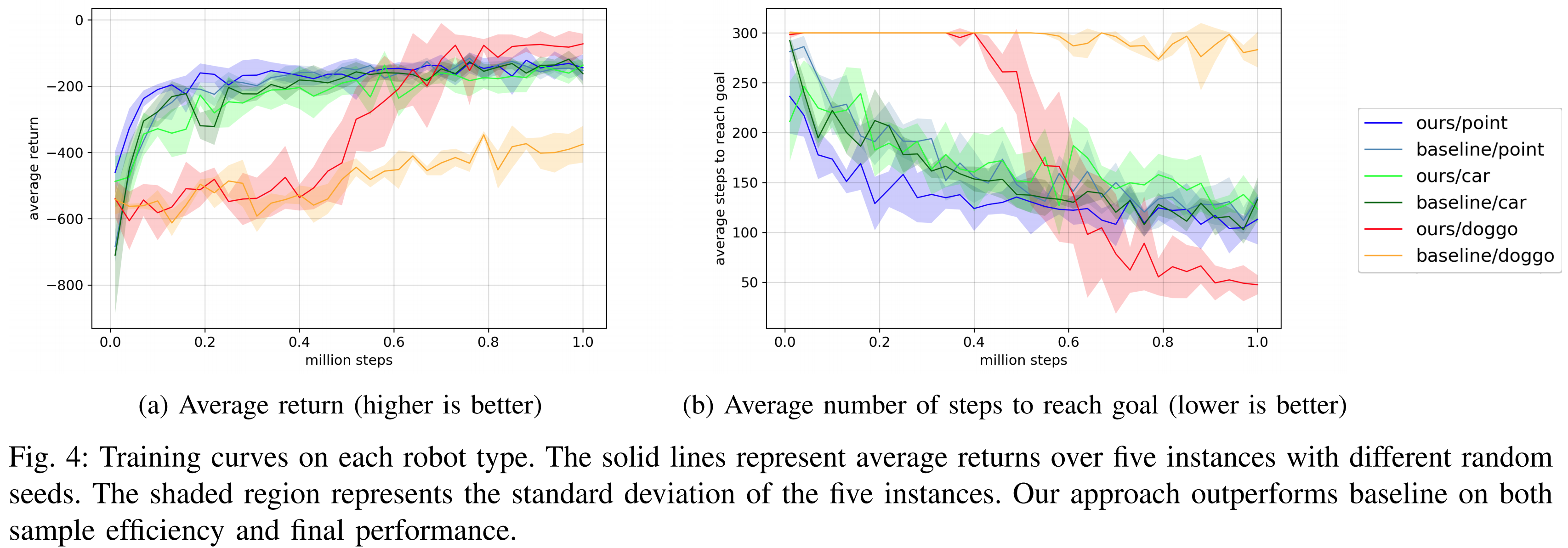
We tested our method on recently proposed Safety Gym, which easily allows to produce different environments with various types of obstacles, and also provides three types of robots (point, car, and doggo). The results shows the sample efficiency is improved.
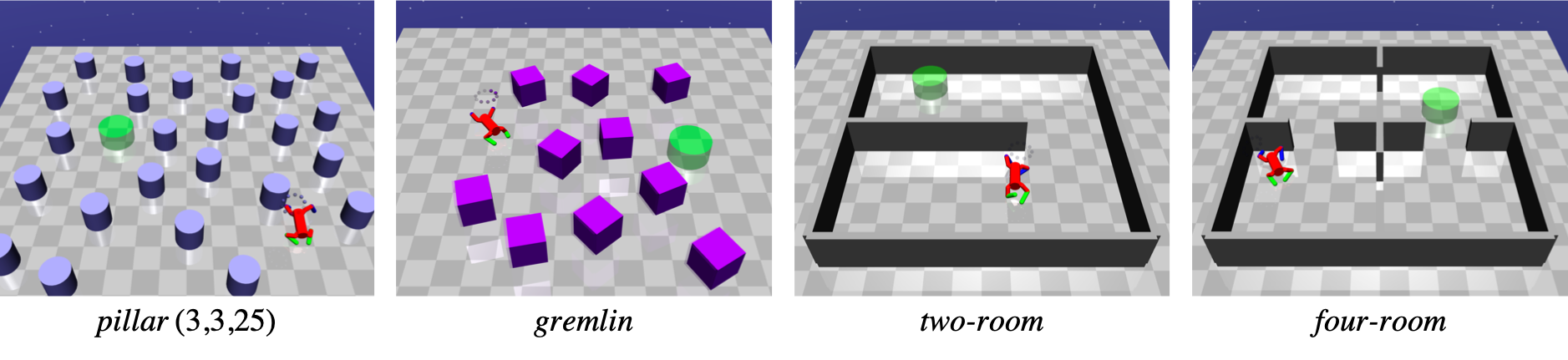
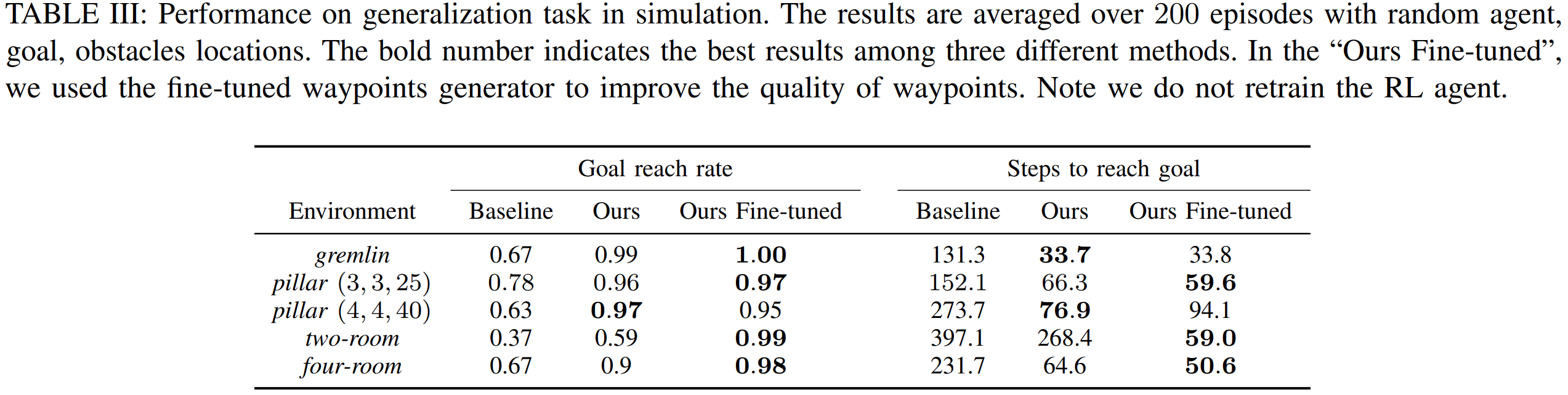
Next, we demonstrated our method also improves generalization capability. We prepared four different types of unseen environments and evaluate goal reach rate and steps to reach goals.
If you are interested in our paper, please check our paper for more details!
